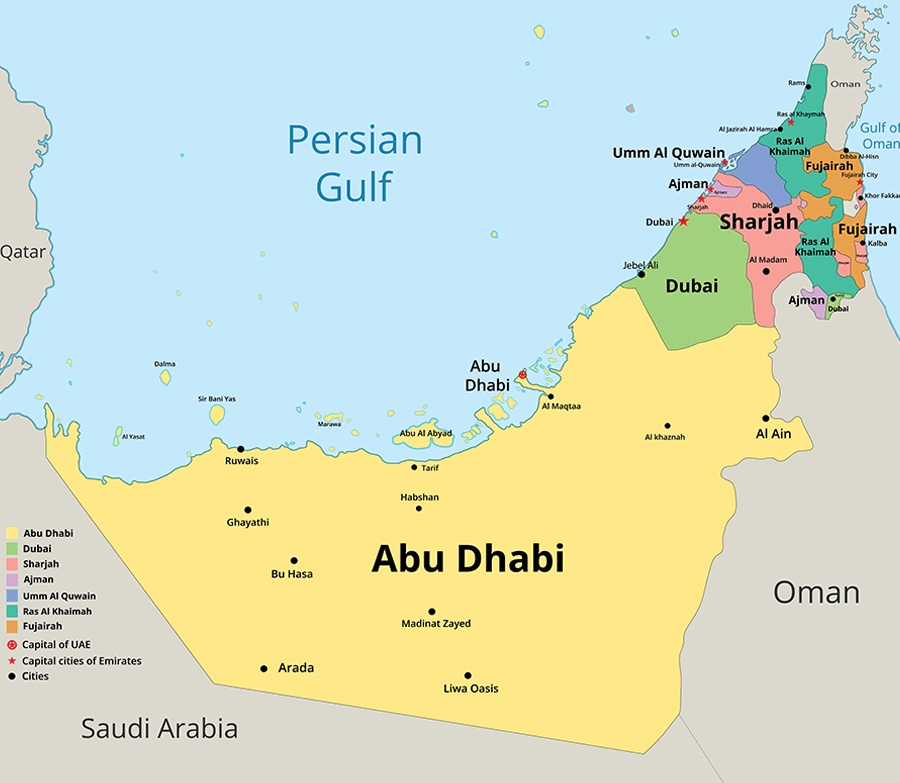
The Seven Emirates of the UAE
When it comes to development, very few countries in the world can match the determination and aspiration that the UAE consistently shows. Its path to glory is nothing short of a fairy tale, supported by the relentless spirit of making a change for the better. It is no wonder that the country today stands as a beacon of success and provides an inspiring blueprint for other nations to emulate.
A pivotal aspect of the UAE that speaks volumes about its strength is its union of the seven emirates. Together, they showcase the diverse and interconnected powers. While each emirate has its distinct beauty and persona, they are all united under the common umbrella of a single motive - to thrive together as a nation.
A closer look at each of them will give you a broader and more in-depth perspective of the country. This is why we are bringing before you a comprehensive guide to the seven emirates of the UAE, wherein you will get to know more about their location, geography, economy, culture, and most importantly, places of interest.
A Brief History of the Arabian Peninsula
The history of the area where the current-day UAE stands can be traced back to 6,000 B.C., when the UAE, as a federation, did not exist. Together with the surrounding region, the area was collectively referred to as the Arabian Peninsula. Early civilisations flourished in the area from the Neolithic or the Palaeolithic Ages (6,000 B.C. – 3,500 B.C.) up to the end of the Iron Age (1,300 B.C. - 300 B.C.).
Envoys from Prophet Mohammed arrived in the area in A.D. 630 and introduced Islam. Soon after that, several European countries arrived in the Arabian Peninsula to explore and assert their dominance over the coasts. The Portuguese, Dutch, and British led control in the Gulf, one after another.
From the beginning of the 18th century to the early years of the 19th century, conflict arose between the British colonial power and the Qawasim section of the Huwalah tribe, who had gained power in the northern and eastern areas of the Arabian Gulf.
After defeating the Qawasims in 1820, a series of agreements was signed between 1820 and 1853 between the British and the sheikhs of the individual emirates to ensure peace at sea. This series of peaceful agreements led to the area being referred to as ‘Trucial States’ or ‘Trucial Coast’.
In 1892, the Trucial States entered into an agreement with the British by virtue of which they could neither enter into any relationship with any foreign government nor dispose of any territories except to the British Government. This continued over the next 75 years until 1968, when the British decided to withdraw from the Gulf region by 1971.
Formation of the UAE
On November 30th, 1971, the British Government left the Trucial States, marking the end of their power over the area. In 1966, the then-ruler of Abu Dhabi, H. H. Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan, championed the cause of a united country. He met with the then-ruler of Dubai, H. H. Sheikh Rashid bin Saeed Al Maktoum, in 1968 to discuss the merger of the emirates that others would be invited to join.
The then-rulers of the other five emirates that formed the Trucial States, along with Bahrain and Qatar, were invited to join in the negotiation. Bahrain and Qatar declared their respective independences. But, six of the seven emirates that we know of today (except Ras Al Khaimah) decided to form a union on July 18th, 1971. On 2nd December, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) was declared as an independent, sovereign, and federal state.
On February 10th, 1972, Ras Al Khaimah (RAK) joined the federation as well resulting in all of the seven emirates that formed the Trucial States, coming together to form the UAE.
A Close Look at the Seven Emirates of the UAE
The UAE is a testament to the strength of unity, as reflected by its dynamic force resulting from the coming together of its seven emirates. Let us take a close look at each of them.
Abu Dhabi
Serving as the federal capital of the UAE, Abu Dhabi also holds the distinction of being the largest emirate of the country, occupying a whopping 84% of the total landmass of the national territory.
With a splendid coastline stretching 700 km., the emirate has a total area of 67,340 sq. km. The city of Abu Dhabi is connected to the mainland by four bridges. They are the Maqta bridge, the Mussafah bridge, the Sheikh Zayed bridge, and the Sheikh Khalifa bridge.
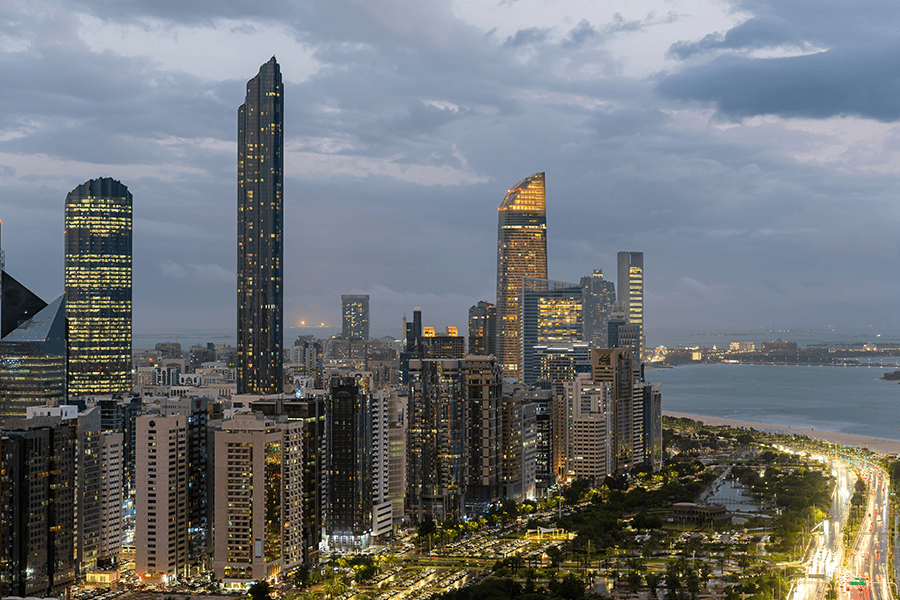

Location and Geography
Resting on the coast of the Arabian Gulf, Abu Dhabi has over 200 islands with its prime cities being Liwa, Ghayathi, Madinat Zayed, Mirfa, Ruwais, Sila and Delma Island. It is bordered by Dubai in the northeast, Saudi Arabia in the south and the west, and Oman in the east.
Its main regions include the City of Abu Dhabi along with Al Dhafrah in the west and Al Ain in the east. Jebel Hafeet is the highest peak of the emirate standing at a height of 1,240 metres.
Economy
Exporting pearls was the main industry of Abu Dhabi before the discovery of oil, after which it became one of the leading producers of energy in the world. It is a pioneer in the global renewable and alternative energy industry as well. You will find the largest solar energy fields in the world here along with the first nuclear energy plan of the Arab world.
A leading financial centre, it is a major contributor to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the UAE. It is also home to the largest stock exchange in the nation - Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM).
Places of Touristic Interest
Abu Dhabi is known for its larger-than-life and splendid sand dunes. The garden city of Al Ain is home to numerous heritage sites. The city also continuously hosts world-class sporting events such as the Formula One Abu Dhabi Grand Prix, the Abu Dhabi Desert Challenge Cross-country Rally, and the Abu Dhabi Golf Championship, among others, bringing thousands of tourists to its shores every year.
Here are some most prominent places of interest in Abu Dhabi.
- Sheikh Zayed National Museum
- Guggenheim Abu Dhabi
- Louvre Abu Dhabi
- Mangrove National Park
- Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque
- Ferrari World
- Warner Bros. World™ Abu Dhabi
- Qasr Al Watan
- Yas Bay Waterfront
- Snow Abu Dhabi
- Yas Island
- Yas Marina Circuit
Dubai
Known as the ‘Pearl of the Gulf’, Dubai is the second largest emirate in the UAE. It covers 4,114 sq. km., which is around 5% of the UAE without the islands.
It is, without a doubt, the face of the Middle East to the rest of the world, establishing itself as a real estate, shopping, and tourism juggernaut. It has catapulted the country to unparalleled global recognition through its rags-to-riches golden storyline and has become a sought-after place to settle down in.
Location and Geography
Located on the eastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, Dubai shares boundaries with Sharjah in the northeast, Abu Dhabi in the south, and Oman in the southeast. Dubai City serves as the capital of Dubai. One of the most prominent geographical traits of the emirate is the historic creek, which divides the city into Deira in the north and Bur Dubai in the south.
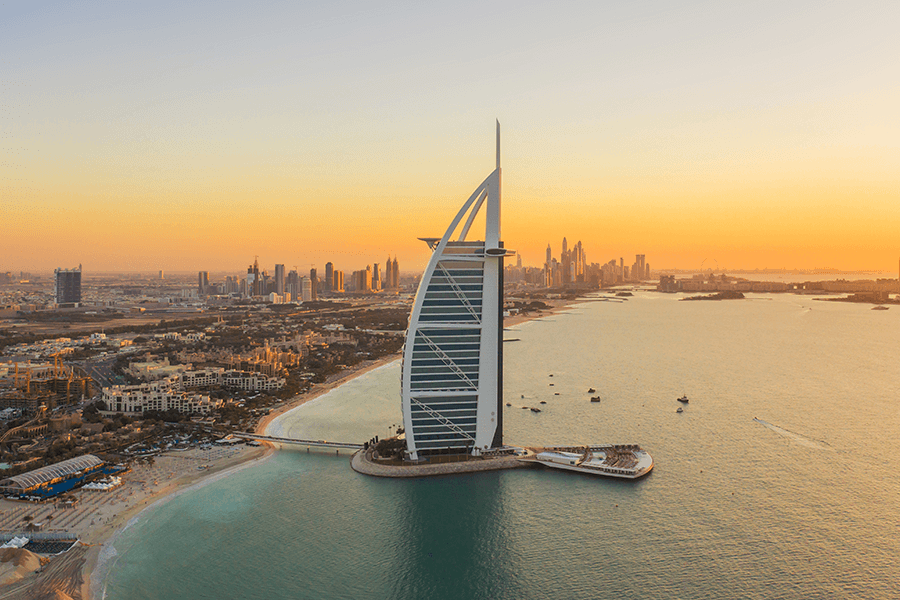

A new addressing system, launched in 2016, divided the emirate into 14 districts. The emirate is known for its diverse landscape. It has mangroves on the eastern end of the reek, sandy beaches on the western side, mesmerising deserts in the western interior regions, and wadis on the Hatta side. Some of the most economically prominent areas of Dubai include Downtown Dubai, Business Bay, JLT, Dubai Marina, and Jumeirah, among others.
Economy
Dubai established itself as one of the busiest ports in the world by the 20th century and was a centre of pearling, fishing, and sea trade. By the 1960s, with the discovery of oil, Dubai experienced a massive transformation that accelerated its development and helped in building the foundation of its modernisation.
It was also the first to establish Islamic banks globally with the launch of the Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB). The first ever global Shari’a-compliant exchange – Dubai Financial Market (DFM) – also served as a wheel of success for the emirate. The city’s diversified economy now stems from its real estate sector, tourism, trade, and services.
Places of Touristic Interest
With a rich history and magnanimous geography, there is no dearth of places of interest in Dubai. You will find the best of the best hotels, entertainment avenues, modern architecture, shopping centres, traditional markets, dining spots, and sporting events in Dubai. On top of that, there are plenty of places to visit for free in Dubai as well.
If you are ever in Dubai, do not miss out on these popular destinations.
- Burj Khalifa
- Burj Al Arab Hotel
- Wadis of Hatta
- Dubai Mall
- Dubai Miracle Garden
- Dubai Frame
- Global Village
- Dubai Aquarium and Underwater Zoo
- Museum of the Future
- Mall of the Emirates
- Dubai Fountain
- Jumeirah Mosque
- Ain Dubai
- Dubai Creek
- Dubai Opera
- IMG Worlds of Adventure
Sharjah
Sharjah is the third largest emirate in the UAE with an area of 2,590 sq. km., which occupies 3.3% of the total area of the UAE without the islands. Known for its picturesque seascapes and landscapes, Sharjah is also popular for being home to the most prominent educational institutions in the country. As such, it ensures a continuous supply of fresh talent in science, engineering, and technology.
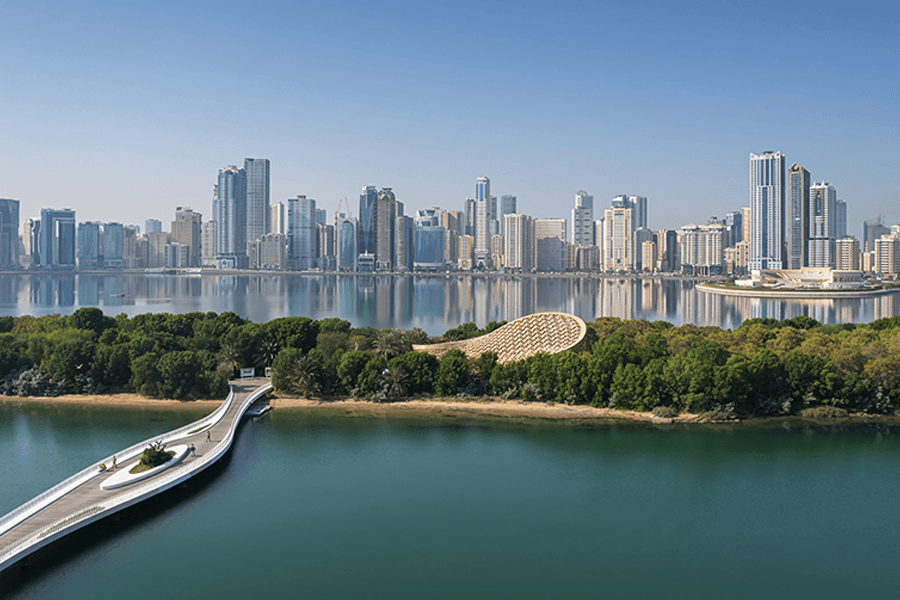

Over the years, Sharjah has been recognised for being the centre of arts and culture, with UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) naming it the ‘Cultural Capital of the Arab World’ in 1998.
Location and Geography
Sharjah is the only emirate of the UAE that lies on both coasts – the Gulf of Oman (Indian Ocean) in the east and the Arabian Gulf in the west. It has various breathtaking desert regions with several agricultural areas. You will find acacia forests, marshes, and pristine beaches in this emirate as well.
It has five major cities, each with its distinct feature. Khor Fakkan is the largest town on the east coast, Kalba is known for its old forts and historical charm, Dibba is a set of three seaside villages, Al Dhaid is the primary producer of fruits and vegetables, and Al Badayer is the most popular desert destination of the emirate.
Economy
Sharjah features three ports and several free zones. Wholesale, retail trade, repair of automobiles, manufacturing, and construction are the major contributors to its economy.
The Expo Centre Sharjah is the most pivotal trade exhibition venue in the region that regularly hosts several B2B (Business to Business) and B2C (Business to Consumers) events. Not to forget, it is also home to popular events such as the Sharjah International Book Fair and Sharjah Biennial.
Places of Touristic Interest
The cultural wealth and architectural heritage of Sharjah is unmistakable. The Organization of Islamic Countries named it the ‘Capital of Islamic Culture’ in 2014. In 2015, it was also conferred the title of ‘Arab Tourism Capital” by the Council of Arab Ministers of Tourism.
If you are coming down to Sharjah, make sure to have the following places of interest in your itinerary.
- Al Qasba
- Sharjah Desert Park
- Sharjah Aquarium
- Al Majaz Waterfront
- Heart of Sharjah
- Al Noor Island
- Buhaira Corniche
- Sharjah National Park
- Blue Souk, Sharjah
- Sharjah Art Foundation
- Sharjah Archaeology Museum
- Souq Al Jubail
- Khalid Lagoon
- Sharjah Safari Park
Ajman
The smallest of the seven emirates, Ajman covers an area of just 260 sq. km., which is roughly 0.3% of the total area of the UAE without the islands. The emirate is distinctly characterised by its rugged and jaw-dropping Hajjar mountain range, although you will find many gorgeous sandy beaches as well.
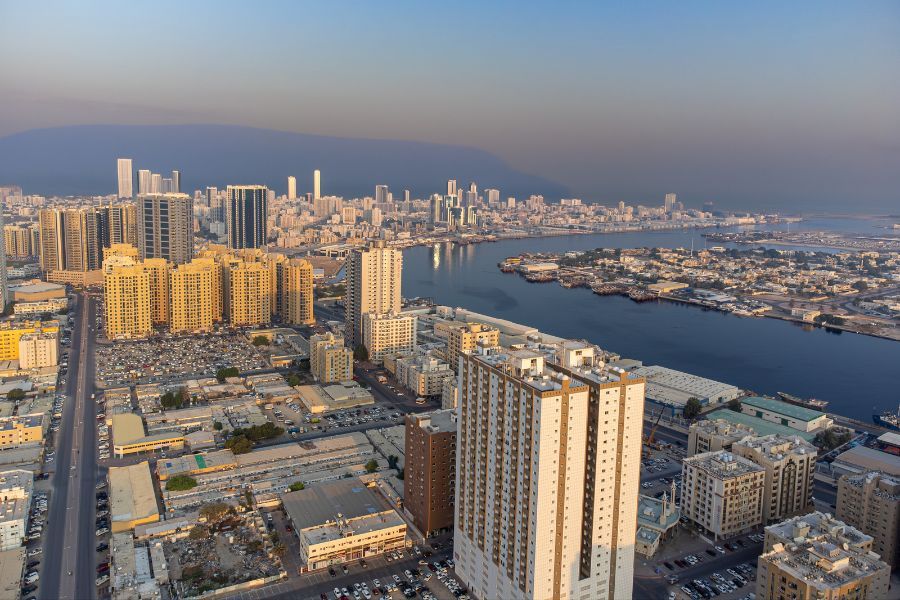

One thing about Ajman which is beloved by tourists is that despite its modernisation and digitisation, it has continued to retain its traditional charm. The fascinating history, gorgeous landscape, and rich culture make this tiny emirate a modern-day paradise.
Location and Geography
Ajman is located on the coast of the Arabian Gulf, in the northern part of the country, to be specific. It lies between the emirates of Umm Al Quwain and Sharjah. The emirate also has a natural harbour on the Arabian Gulf.
Among its main cities, the most notable one is Ajman City, which is the commercial hub and has a broad range of banks, companies, and the Ruler’s office. Al Manamah City is famous for its high mountains and valleys, rich in chromate and magnesium. Masfout City is known for its agriculture and has beautiful mountains such as Leshan and Dafta, along with wide valleys such as Ghalfa.
Economy
Ajman is well-connected to the other parts of the country and the world through the Ajman Port and Ajman Free Zone. Both of them play vital roles in the economic growth of the emirate. The free zone supports hundreds of industrial companies and offers profitable options due to their low operational costs.
Manufacturing industries, wholesale, retail, automobile repair, and construction sectors are all major contributors to the GDP of Ajman. In recent years, a major focus has been shifted to innovation and sustainability, hoping to attract investments.
Places of Touristic Interest
The white sandy beaches of Ajman are a sight to behold. The serene ambience, clear water, and fresh air of the whimsical beaches will leave you spellbound. Sea lovers will enjoy the adrenaline-rushing as well as calming marine activities that they can participate in. Known for its exceptional hospitality, you will never run out of options to explore in this emirate – be it beaches, mangroves, malls, or museums, among others.
Make sure to visit the following places of interest while in Ajman.
- Saleh Souk
- Al Zorah Nature Reserve
- The Red Fort
- Masfout Gate
- Masfout Castle
- Ajman Museum
- Safeer Mall
- Aqua Bounce Ajman
- Ajman Marina
- Al Murabbaa Watchtower
- Al Zorah Golf Club
- Ajman Corniche
Umm Al Quwain
The second smallest emirate of the UAE, Umm Al Quwain, is also the least populated emirate of the country. Covering an area of around 720 sq. km., it makes up for 1% of UAE. Deemed as the perfect blend of opportunities and tranquillity, it is ideal for those who are looking for a peaceful retreat.
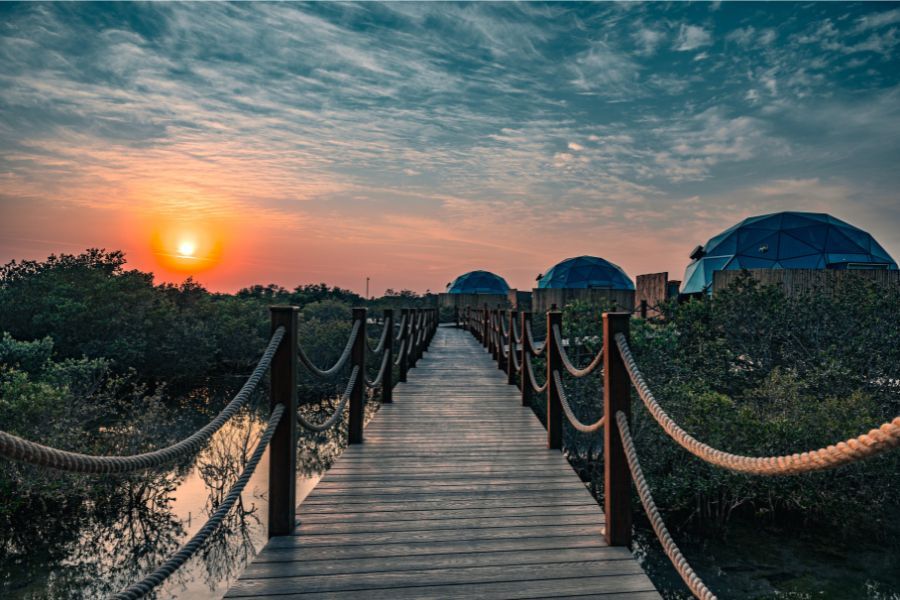

Umm Al Quwain also holds the distinction of being the most ancient emirate of the nation as archaeological studies have suggested its relation with Mesopotamia during the third millennium B.C.
Location and Geography
Umm Al Quwain is located between Ras Al Khaimah to its northeast and Sharjah to its southwest. The City of Umm Al Quwain, which serves as its capital, is built on a narrow peninsula known as Khor Al Bidiyah. It has a beautiful coastline that stretches for about 24 km.
Situated in the northern part of the UAE, this emirate is triangular in shape. As for its vegetation, it comprises rich coastal mangroves along the fertile oases inland and Arabian Gulf. Being one of the lesser-known emirates of the country makes it even more appealing.
Economy
Fishing is one of the primary contributors to its economy, and it exports seafood across the Middle East and Europe. Falaj Al Mualla is also home to the first poultry farm in the UAE. The Umm Al Quwain Free Zone (UAQFTZ) is the most thriving business hub in the emirate, attracting both local and foreign businesses.
In recent years, it has been striving to develop a blue economy, which focuses on the sustainable use of ocean resources to facilitate economic growth and provide jobs. As such, preserving the marine ecosystem is a key priority for the emirate. Plans for economic diversification are also in place to attract more investments from all corners.
Places of Touristic Interest
With rich coastal mangroves on the coast of the Arabian Gulf and numerous gorgeous islands on the east of the mainland, Umm Al Quwain provides a plethora of options for you the explore as a tourist. Additionally, the emirate also facilitates various recreational activities on its beaches and clubs including waterskiing, sailing, windsurfing, and horse-riding, among others.
Here are some of the must-visit places of tourist interest in Umm Al Quwain.
- Jazirat Al Ghalla
- Al Sinniyah
- Al Sow
- Al Qaram
- Al Chewria
- Al Keabe
- Al Humaidi
- Al Harmala
- Dreamland Aqua Park
- Umm Al Quwain Aeroclub
- Falaj Al Mu'alla
- Tell Abraq
- Ed Dur
- Umm Al Quwain National Museum
- Alokaaab Island
- Falaj Al Mualla Fort
Ras Al Khaimah
The fourth-largest emirate of the country, Ras Al Khaimah, covers an area of 1,694 sq. km., which makes up 3.16% of the UAE’s total area. The emirate will blow you away with its varied topography, ranging from mountains to rolling sand dunes, and even pristine beaches. With a rich history dating back 7,000 years, Ras Al Khaimah has been establishing itself as a real estate powerhouse in recent years.
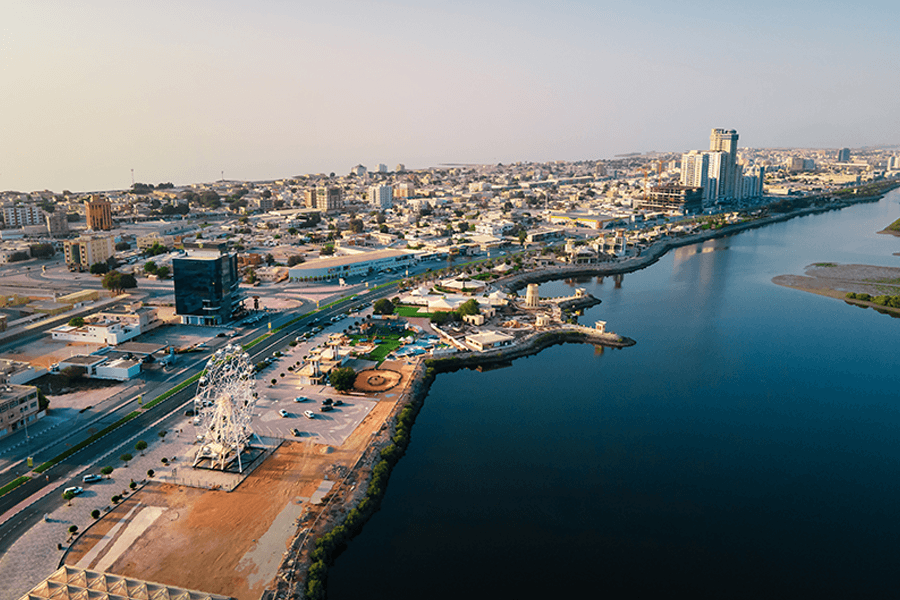

Known for having around 1,000 archaeological sites, the emirate has, to date, preserved many traditional fishing villages in the Arabian Gulf, Al Jazirah Al Hamra. In addition, it is also home to the 18th-century Dhayah Fort, which is the only hilltop fort still in existence in the country. GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) has recognised Ras Al Khaimah as the Gulf Tourism Capital for both 2020 and 2021, which speaks volumes about its tourism prospects.
Location and Geography
The northernmost emirate of the country, Ras Al Khaimah shares domestic borders with Sharjah, Umm Al Quwain, and Fujairah, and international borders with Oman. A creek divides the emirate into two distinct areas – the western old town of Ras Al Khaimah and Al Nakheel on the easter side. Some of the other major towns of the emirate are Masafi, Khatt, Digdaga, and Al Jazirah Al Hamra.
One of its most distinct areas is Al Marjan Island, an archipelago made of four man-made coral-shaped islands. This island offers unprecedented real estate offerings by top property developers, hospitality services through world-class hotels, resorts and spas, and lifestyle retreats through its myriad of entertainment and recreational avenues.
Economy
Economic diversification has led to exponential growth of the economy of Ras Al Khaimah. From SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises) to multinational companies, organizations and businesses of varied sizes have successfully launched themselves, thanks to the establishment of free zones and industrial areas in the emirate.
Tourism is the primary contributor to its economy, which has also perpetuated the growth of the real estate sector, making investments in Ras Al Khaimah a profitable opportunity. Furthermore, Ras Al Khaimah Economic Zone (RAKEZ) provides personalised solutions to free zone as well as non-free zone businesses in more than 50 countries. Manufacturing industries of construction materials, ceramics, petrochemicals, and pharmaceuticals heavily boost the economy of the emirate as well.
Places of Touristic Interest
The mountains and desert offer opportunities for nature trails and safaris while the beaches and main city provide amenities for carrying out varied leisure activities. Engage in horse riding, museum visits, wadi adventures, and ruins exploration while on a trip to this emirate.
Take a look at the must-visit places of interest in Ras Al Khaimah.
- National Museum of Ras Al Khaimah
- Pearl Museum
- Jebel Jais
- Dhayah Fort
- Hot springs at Ain Khatt
- Al Wadi Equestrian Adventure Centre
- Mohammed Bin Salem Mosque
- Manar Mall
- Al Naeem Mall
- RAK Mall
- Al Hamra Mall
- Iceland Water Park
- Flamingo Beach
- Ras Al Khor Wildlife Sanctuary
Fujairah
One of the coolest emirates of the country owing to its easterly location, Fujairah covers an area of 1,450 sq. km. It also experiences higher rainfall than anywhere else in the country. The emirate boasts of a rich history that dates back to 3,000 B.C. when it was inhabited by fishermen and herders and was known as 'Ard Al Jababerah' which translates to the ‘Land of the Titans’.
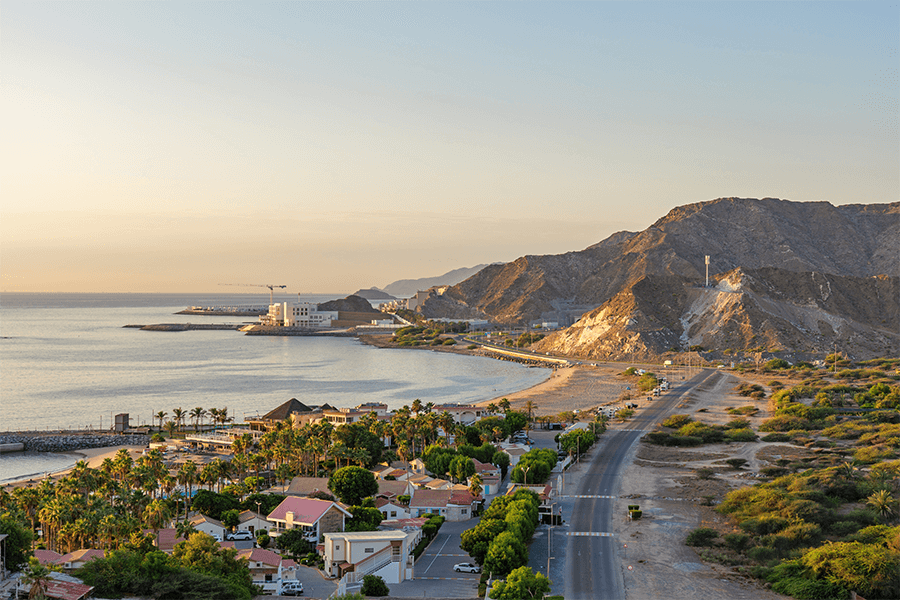

Mountains cover most of the emirate with the Al Hajar Mountains separating it from the rest of the UAE. Although it does not have any desert, you will find plenty of beaches for leisure here. History and natural landscapes encapsulate the charm of Fujairah, making it a worthy destination.
Location and Geography
Fujairah is the only emirate located on the eastern coast of the UAE along the Gulf of Oman. Additionally, it also means it is the only emirate in the country with no territory on the Arabian Gulf. Its distinct geography separates it from its fellow emirates, giving it quite a unique identity. Internationally, it shares a border with Oman.
The Hajjar Mountains form a natural barrier on the western side of the emirate. Its shores extend along the Gulf of Oman for approximately 70 km. from the City of Fujairah in the south to the town of Dibba in the extreme north. Fujairah City and Dibba Al-Fujairah are the two main cities in the emirate, with other prominent towns and villages being Al Badiyah, Al Aqah, Masafi, and Tawain.
Economy
The economy of Fujairah is heavily dependent on fishing and agriculture. The Fujairah Free Zone, which surrounds the Port of Fujairah, facilitates foreign investment in trade and banking. The ‘Fujairah Plan 2040’, launched in 2015, aims to add new terminals for oil, dry bulk, marine services, and containers to add to the development of the Fujairah Port.
Since Fujairah is the only access of the country to the Indian Ocean, it has extreme strategic relevance. It operates a multipurpose port that provides easy access to the most pivotal shipping routes in the world. It is also home to the largest livestock shipping companies in the world. Mining and stone crushing also contribute to the economy of the emirate.
Places of Touristic Interest
Be it the rugged mountains or the stunning oases, the enthralling waterfalls or the splendid valleys, the pristine sandy beaches or the soothing hot, cold, and mineral springs, Fujairah is gorgeous through and through. Its moderate climate makes it more palatable to global visitors as well.
If you are visiting Fujairah, make sure to include the following in your list.
- Wadi Al Wurayah Waterfalls
- Fujairah Fort
- Ain Al Madhab Gardens
- Al Bidya Mosque
- Fujairah City Centre
- Kalba Corniche Park
- Lulu Mall
- Umbrella Beach
- Al Hayl Castle
- Fujairah Museum
- Friday Market
- Fujairah Heritage Village
- Snoopy Island
- Madhab Sulphur Springs
- Tim’s Reef
To Conclude
The fast-paced development that the UAE has experienced is largely contributed to by the unity of its seven emirates, with each of them working together in unison to strive for modernism while upholding traditional values. Having distinct personas, each emirate tells a different story. With their diverse topography and economy, they provide endless tourism opportunities along with the hope of a better life.
So, come and explore the seven emirates of the UAE. Witness the natural beauties and mesmerise yourself with the stunning man-made architecture. While at it, familiarise yourself with the career opportunities they provide that make settling down in them a worthy option.
FAQs
What are the seven emirates of the UAE?
The seven emirates of the UAE, in alphabetical order, are Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah, Sharjah, and Umm Al Quwain.
Which is the richest emirate in the UAE?
In terms of per capita income as well as GDP, Abu Dhabi is the richest emirate in the UAE. Being the largest emirate of the country, it is a major contributor to the nation’s overall economy. It is also a leading oil producer and has made commendable strives to diversify its economy through investments in varied sectors such as tourism and financial services.
Which is the biggest emirate in the UAE?
The biggest emirate in the UAE, in terms of landmass, is Abu Dhabi. With a total area of 67,340 sq. km., it occupies 84% of the national landmass territory of the country.
Which is the smallest emirate in the UAE?
The smallest emirate in the UAE, in terms of area size, is Ajman. With an area of just 260 sq. km., it covers only 0.3% of the UAE’s area without the islands.
Who is the king of Dubai?
At present, the king or ruler of Dubai is H.H. Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum. He also serves as the vice president and prime minister of the UAE.
What is the history of the UAE?
The UAE was formed on December 2nd, 1971, when six of the seven emirates - Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Dubai, Fujairah, Sharjah, and Umm Al Quwain - that were previously known as the Trucial States under British protection, joined forces to come together as a single federation.
The seventh emirate, Ras Al Khaimah, joined the federation seven months later on February 10th, 1972, to shape the present-day UAE as we know it today.
What are the main tourist attractions in the UAE?
The UAE is known for its splendid natural landscape and stunning man-made architecture. Some of the most popular tourist attractions in the country that you can’t afford to miss are as follows.
- Burj Khalifa
- Louvre Abu Dhabi
- Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque
- Dubai Mall
- Ferrari World
- Dreamland Aqua Park
- Jebel Jais
- Sharjah Art Museum
- Jebel Hafeet
- Wadi Al Wurayah Waterfalls
- Ain Al Madhab Gardens
- Qasr Al Watan
- Yas Island
- Souk Madinat, Jumeirah
- The Museum of The Future
- Etihad Towers Observation Deck
- Warner Bros. World, Abu Dhabi
- Jumeirah Public Beach
- Corniche Beach
- Al Hamriyah Beach




