Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan
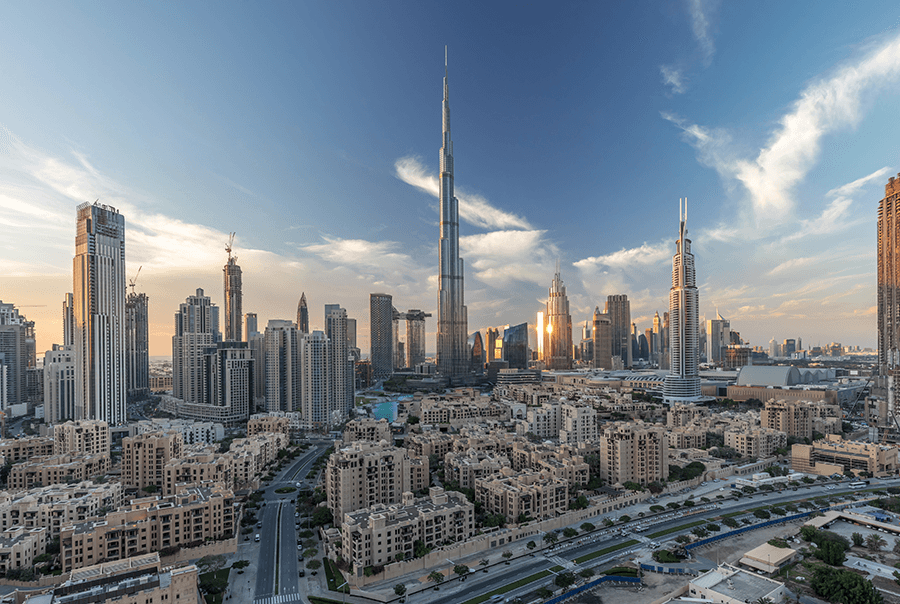

Dubai's global appeal and dominance stem from years of planned and meticulous development. The greatness it has achieved so far has been shaped by long-term vision, robust leadership, and sustainable planning, and it plans to continue this development. The foundation of the upcoming development of the city is governed by the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan.
Aimed at making the city more liveable and comfortable for its citizens, the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan sets the tone for the strategic structural layout of the city. Celebrating the rich history of Dubai, it also sets an ambitious agenda to improve the overall environment of the city while making provisions to pave the way for infrastructural efficiency.
In this space, we will get a deep dive into what this plan stands for, what are its objectives, what sort of outcomes can be expected from its execution, and how important it is for the city’s future. Besides, we also are going to look into the population growth plans, 2040 structure plan, and Hatta development plan, along with other allied adjacent pillars.
What is the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan?
The Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan is a comprehensive strategy that outlines how Dubai will evolve over the next two decades. It is essentially a 20-year integrated roadmap to realise the urban development agenda of the emirate. The plan serves as the primary tool for the government to mobilise the spatial initiatives in its renewed planning system for both metropolitan Dubai and Hatta.
It is the sixth developmental plan for the city since 1960. The master plan focuses on improving the quality of life for the residents of the city and aims at enhancing their happiness. It has been designed to reinforce Dubai once again as the ultimate global urban destination for the city over the next 20 years.
The plan aligns seamlessly with the strategic economic priorities of the city while also keeping in mind its future needs. At the same time, it integrates all urban development master plans in the city. Since Dubai anticipates doubling its residential population in the next few years, this plan is believed to help the city embark on a future-proofed and sustainable growth path in the face of game-changing technological, environmental, and economic opportunities.
Objectives of Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan
The Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan succinctly lays out the objectives it needs to fulfil to facilitate the sustainable urban development of the city. Let us take a closer look at the objectives of the plan.
Upgrade Urban Areas
One of the primary objectives of the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan is to modernize and improve the liveability conditions of historically significant and older areas of the city while also introducing new development hubs.
It is believed that revitalizing the older areas will create more employment opportunities, upgrade infrastructure, and offer enhanced public spaces, thereby fostering a culturally rich yet modern urban ambience.
Resource Efficiency
The plan aims to significantly lower resource consumption and wastage and promote sustainability in the process. It encourages a transition towards renewable sources of energy, such as solar power and maximizes its usage in buildings and transport.
Furthermore, it emphasizes reducing and recycling landfill waste through sustainable construction mechanisms. These steps will lead to a more eco-conscious lifestyle and lower environmental impact while also reducing utility costs for residents.
Develop Vibrant Communities
There is a heavy focus on developing vibrant communities that are healthy, inclusive, and offer access to ample recreational spaces. There are plans to multiply the number of green spaces in the city and encourage outdoor activities and overall well-being.
Additionally, the plan makes sure everyone has access to education, health services, and leisure spaces irrespective of their income. All these will lead to stronger community ties, improved air quality, and more recreational activities.
Sustainable Mobility
The Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan looks forward to having 55% of its residents within walking distance of public transportation stations, thereby reducing the need for private cars. This will help in lowering traffic congestion and improve environmental impact.
By developing more cycling and walking paths, the plan will help promote non-motorized travel, which, in turn, will bring environmental and health benefits. Residents will be able to enjoy cheap commuting with less pollution and traffic.
Foster Economic Growth
There will be an increased focus on encouraging foreign investment in green energy, technology, and innovative industries, which will help in diversifying and stimulating the city’s economy. It will lead to more job opportunities in emerging industries across varied fields.
The increased economic activity will help in offering conducive career prospects for the people of the city. In the process, Dubai’s status as a strong business hub will prevail.
Enhance Environmental Sustainability
This smart and futuristic vision plan aims to make sure that the future development of Dubai is aligned with environmental protection and sustainability. It plans to dedicate 60% of the city’s land to natural reserves, rural areas, and green spaces. There are provisions in place to build systems that will not only monitor but also improve water and air quality across the city.
As such, people will have access to cleaner and more breathable air and better water quality. Residents of the city will also have more accessible natural areas, which will dramatically improve the overall quality of life.
Preserve Cultural and Urban Heritage
Apart from the environmental concerns, the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan also hopes to restore and protect old neighbourhoods in the city to maintain its cultural identity. There will be more emphasis put on conserving areas and preserving their historical significance while also modernizing infrastructure.
There are plans in place to foster a sense of connection and pride in the history of Dubai among people by retaining cultural landmarks. The plan promotes a healthy balance between modernity and tradition.
Governance and Legislation
The plan aims to strengthen and secure governance and legal frameworks in the city that will ensure sustainable and smooth urban growth. There will be new and comprehensive urban planning laws in place that will help regulate development and make sure that growth meets the long-term sustainable objectives of the city.
With a focus on transparent governance models, it is believed urban projects will be ethically and efficiently executed. These steps will help foster the trust of residents in local governance.
Major Outcomes of the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan
With the help of the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan, the city hopes to become a more sustainable, liveable, and economically robust place. It does so by taking initiatives that will enable positive outcomes. Let us take a look at some of the major outcomes that this plan hopes to achieve.
Doubling Green Spaces
Get ready for an even greener Dubai as this plan aims to double the size of green and recreational areas, offering more natural spaces for the residents to enjoy. With 60% of the emirate’s land being dedicated to rural and natural spaces, there will be a positive balance between the natural environment and urban development.
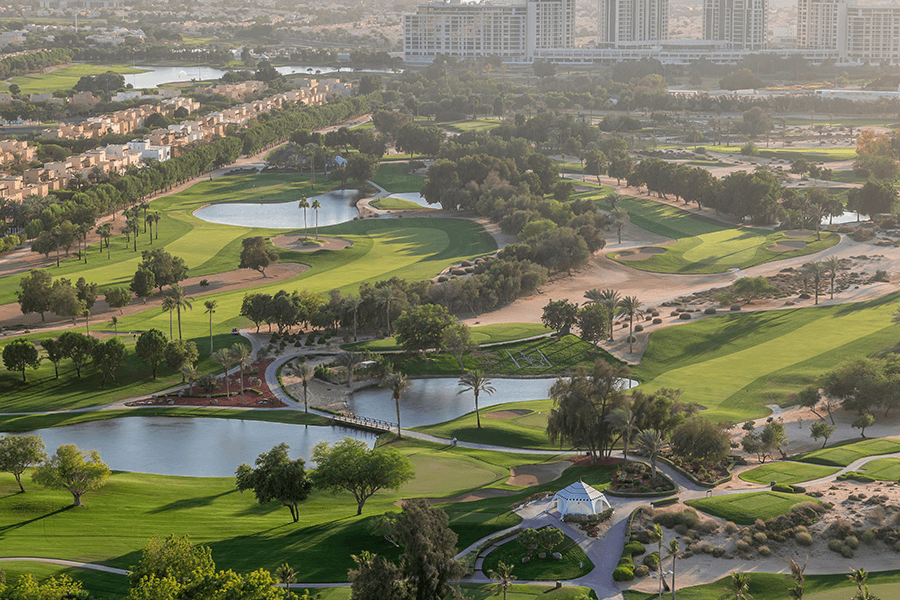

Green Corridors
Good news for everyone who loves taking a stroll or a bike ride by the city as the plan aims to introduce green corridors across Dubai. These corridors or eco-friendly pathways will encourage cycling, boost walkability, and link neighbourhoods with workplaces and service areas. There will be less dependency on private cars to move around, thereby contributing to a healthier lifestyle.
Increased Land for Tourism and Commerce
The tourism and commercial sectors of the city are expected to grow further with this plan as it will increase the land for hotels as well as commercial areas. This also means that there will be increased employment opportunities for residents who can thrive in these profitable industries. Additionally, tourists will get to experience world-class offerings.
Expansion of Education and Health Facilities
The plan also takes into consideration education and health facilities with more land being dedicated to these two sectors. Therefore, more top-tier educational establishments and better medical services will be available to meet the increased and rapidly evolving population of the city.
Extended Public Beaches
The coastline of Dubai is one of its most enviable features, and the plan incorporates multiplying the public beaches, giving unprecedented access to residents and tourists to the stunning coastline of the city. This expansion will make Dubai a dream travel destination for beach lovers if it is not already.
Importance of the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan
The Government of Dubai has been producing urban plans since 1960 that have helped in evolving the emirate from its humble roots to the dynamic global city as the world knows it today. The Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan is the sixth such plan and it takes on the DNA of the previous plans to guide the city to a confident future.
The plan will coordinatingly direct development through its structured approach and varied principles, strategies, initiatives, and policy directions. It will not only enhance the environment of the city by improving the ease of conducting business and facilitating infrastructure efficiency, housing choices, and park provisions but it will also celebrate the rich history of the emirate.
As the city expects to double its population in the next few years, this plan will serve as a blueprint to face the challenges of an ever-evolving migration. It will give fuel to economic and technological opportunities while being conscious of environmental protection and sustainability.
By taking a people and environment-centric approach, the plan will act as a spatial roadmap for the upcoming 20 years and thereby advance sustainability, cohesiveness, and prosperity. Through its guided planning, it creates a visionary framework and spells out the core objectives to promote social, economic, cultural, and environmental well-being.
Population Growth Plans
Keeping in mind the socio-economic conditions, the plan offers a preliminary forecast of Dubai’s growth in the upcoming 20 years. It provides detailed employment, residents, and visitor population forecasts to estimate the land and floor space requirement. The population growth of the city is believed to stay highly responsive to its development.
It is estimated that the residential population of Dubai will reach 7.8 million by 2040. There will be increased land requirements since most of the employment will be generated by knowledge-focused and high-tech economic sectors. Daily visitors to Dubai are also predicted to increase, thanks to the appeal of the city as a global aviation and tourism hub. This means that there will be an increased demand for hospitality services.
Even though the requirements may seem remarkable, they do not exceed the quantum of unbuilt land that was previously allocated for future development. As such, there are still opportunities for sustainability. The requirements state the need to manage future growth, which can be done by exploring innovative and new avenues to refocus developmental plans.
The 2040 Structure Plan
The 2040 Structure Plan encapsulates the spatial directions, strategy themes, and sustainable growth principles to facilitate the growth of the emirate. It takes into consideration the following highest-performing components to bring in development.
Spatial Structure
The plan embodies a people-centric hierarchy of centres with each of them offering a wide range of essential services, employment opportunities, and other allied key elements. It facilitates transit-oriented development.
Sustainable utility provision is encouraged through land allocation to produce renewable energy. It classifies the emirate into four separate development areas to help manage growth while also conserving the natural habitat.
Additionally, it designates unzoned land in rural areas for wilderness and precludes them from future development. It sets out the 2040 development footprint to make sure the future growth aligns with the increasing demand in every sector.
Centres
Centres refer to the mixed-use areas that focus on employment, services, and leisure opportunities in concentrated areas. They serve as the key building blocks of the spatial structure of the plan. The plan aims to bring residents close to their workplaces and shopping centres. Furthermore, it also heightens the utility of public transport investments and lowers sprawl by consolidating development.
Essentially, the plan proposes a hierarchy of centres. The higher-order centres include urban centres, multi-sector centres, and sector centres. These centres accommodate an eclectic range of higher residential density, city-serving activities, and a major percentage of employment to residential uses that help bridge the proximity of residents to their jobs.
The other aspect comprises the district community and neighbourhood centres that cater to the daily needs of residents in their immediate vicinity. The centres function as the pivotal element of the transit-oriented development approach of the plan.
People-Centric Design Approach
By adopting a people-centric design approach across varied dimensions, the plan is expected to be complemented by various sectoral strategies. Currently, the population density is unevenly distributed, which results in a fragmented urban system. In the future, this population density will be evenly densified and distributed at different centres to reinforce pedestrian-friendly streets.
Similarly, at present, the mixed-use development areas do not create a cohesive urban fabric since they are extremely disjointed. But, in future, the distribution of mixed-use development will be based on increasing green and open spaces while also creating active ground floor uses.
Housing
The housing landscape of Dubai is extremely varied and showcases the diverse backgrounds and lifestyles of the emirate’s demographic makeup. At present, there are inconsistencies in housing densities near transit stations. Labour accommodation lacks mass transit access and commercial amenities since they are built next to or within industrial areas.
In the future, there are plans to prioritize housing within designated growth areas that are close to or within the centres. The plan also makes sure that the supply of housing aligns with the demand. At the same time, it also ensures the growth is staged so that the pipeline can meet the forecasts of population growth.
Focus on providing affordable housing options and allocating staff adequate housing near centres are also there. It hopes to allow residents to have access to economical housing options along with amenities, jobs, and public transit access.

Employment
In terms of offices, the plan seeks spatial growth of job sectors and aims to bring residents close to their jobs. There will be better connectivity and enhanced integration between employment locations and residential spaces as the vast majority of future office developments will be within or near the centres.
Being a global shopping destination, the plan proposes to manage the retail supply in Dubai sustainably. All residents will be within a short cycle trip or walking distance of essential retail services. Future hospitality will also be allocated in centres and several tourism zones will be created across the city.
The plan identifies numerous transit-accessible industrial districts in the urban core as mixed-use regeneration districts by employing schemes of holistic redevelopment. Additionally, it also positions the southern emirate as a multi-modal production and logistics hub.
Open Space
The open space aspect of the plan intends to increase the number of green spaces in the urban area of the emirate. It pushes for an increase in the number of publicly accessible parks and recreational spaces. There are plans to introduce desert, marine, and conservation parks. These will be designated for protection with minimal, controlled, and sustainably managed public use.
There are provisions in place to expand green corridors and connectors. These will connect major parks, significant natural assets, and centres. In addition, there are plans to enhance access to public beaches by linking existing waterfront to urban areas through these green corridors.
Community Facilities
A major facilitator of a people-centric liveable city in a post-pandemic world is its ability to offer a broad array of employment and essential services opportunities within close reach of homes. This plan proposes a 20-minute city concept wherein the majority of employment opportunities, amenities, and services are within a 20-minute cycle trip or walk.
It also makes sure that lower-order facilities can be accessed through short walks whereas higher-order amenities can be accessible by a 30-minute public transit trip. In addition, there are also plans to make sure all residents are within a 30-minute metro or light rail trip to their workplaces.
Environment
As the plan takes environmentally conscious decisions, it is no surprise that it aims for reduced emissions, avoids fragmentation, and enhances resource efficiency. It does so by involving directions in three major areas.
First, it addresses environmental quality, sustainability, and urban connectivity. It aims to build closed systems for resources through recycled and stormwater treatment and maximizing water storage capacity. Secondly, it addresses natural conservation and ecological connectivity by potentially expanding Natural Conservation Areas (NCAS) and allocating unzoned rural land as wilderness with limited future development.
Thirdly, it addresses environmental planning and management. It does so by ensuring all framework plans are subjected to the process of Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA). Additionally, it makes sure that spatial plans based on environmental data are integrated into the geospatial datasets of Dubai.
Mobility
The transportation system of the city has been taken into consideration as well in the formulation of the plan. Starting with soft mobility, there are plans to develop a permeable pedestrian network that connects residents with essential services. Plans for building shaded soft mobility routes are also there to mitigate the urban heat island effect.
For public transport, lower-order centres are to be connected by bus and soft mobility while higher-order centres are to be connected by metro or light rail. Coming to private transport, it is believed that increasing public transit access to centres will lower automobile demand, thereby leading to eco-friendly choices.
The plan also reserves sites in industrial areas for fulfilment centres while also advocating for autonomous truck and delivery systems. It also prioritizes logistics along the Jebel Ali/ Al Maktoum Airport inter-modal hub and Etihad Rail alignment.
Utilities
The plan directs its focus on all major utility pillars to facilitate sustainable development. To start with power and potable water, the plan reinforces the ongoing implementation of the Dubai Demand Side Management (DSM) strategy, initiatives, and programs. It also supports the efforts of the Dubai Clean Energy Strategy 2050 initiatives.
Next up, it addresses sewerage by extending its support to direct the demand for future sewerage to the Sewage Treatment Plans (STPs) of the emirate. It also plans to improve the urban detention and discharge systems of stormwater. It aims to facilitate district cooling through a recycled water supply network and regulate the tariff structure as it will help achieve an economically viable and efficient system.
As for solid wastes, it recommends various locations to host new recycling plants, landfills, waste-to-energy sites, and other allied waste management facilities.
Integrated Rights of Way
The Structure Plan 2040 paves the way for integrating the Rights of Way (RoW) for mobility, utility, and green infrastructure to achieve four objectives. First, it wants to maintain the sufficiency and continuity of corridors to reinforce future and projected growth. Second, it aims to align with the utility and RoW system of the emirate.
Third, it intends to improve open space along with utility and connectivity via holistic links across Dubai. Fourthly, it wants to maintain efficiency with minimal impact on all other features within the corridor.
The plan prioritizes cyclists and pedestrians within the RoW by paving the way for more mobility options without sacrificing comfort or safety. It elaborates on the design of present and future RoWs by categorizing them depending on their locations to bring about more flexibility in their designs.
Hatta Development Plan
Hatta refers to the inland exclave of Dubai, which lies in its southeast section. The Hatta Development Plan spells out the direction that will lead to the growth of Hatta to support continued liveability in the area. It focuses on the future growth of self-reliant sustainable and compact urban villages in the agricultural-focused environs of the exclave.
In addition, there are talks of boosting the local economy by using the natural assets and heritage of Hatta through community-focused eco-tourism. The plan aims to responsibly and resiliently manage the growth of Hatta by protecting its unique natural assets and inducing high-quality housing options. It intends to support the role of Hatta as a strategic regional centre.
The spatial concept of the plan ensures development is restricted to low-slope areas outside Wadis. In addition, it aims to develop small-scale rural centres and provide diverse employment opportunities for its residents.
New Tourism Projects in Hatta
Boosting the tourism sector in Hatta is a key goal of this plan and the array of new and upcoming tourism projects in Hatta attests to this objective. From the Hatta Sustainable Waterfalls to the 5.4 Km chairlift system, from the 120 Km bicycle paths to the new hiking trails up to Jebel Umm Al Nisour, these projects cover varied aspects. Not to forget, the development of an international hotel is going to take care of the hospitality factor as well.
Local Farming Experience Program
The Local Farming Experience Program highlights the focus on the agricultural aspect of Hatta and introduces new and scientific methods to farmers to help them achieve better production yields.
Hatta Sustainable Waterfalls
The Hatta Sustainable Waterfalls project has been designed to create an artificial waterfall using the dam’s slope. The water from the waterfall will be tactfully collected at the stream's end before being recycled and pumped back to the top of the waterfall again.
The Chairlift Line
The chairlift line is being designed to cross the Hatta Dam Lake and Upper Dam Lake, which is part of the DEWA (Dubai Electricity and Water Authority) hydroelectric project, to connect to the summit. The plan is to construct a departure station above the Hatta Dam on a platform.
Sky Bridge
There is a plan to build a sky bridge and an observation deck on Jebel Umm Al Nisour. This peak, which stands at 1,300 metres above sea level is the highest natural peak in Dubai. This project is collectively called the Dubai Mountain Peak.
Direct Bus Service from Dubai to Hatta
There is a direct bus service being planned from Dubai to Hatta. This bus service will enable passengers to carry their scooters and bicycles onboard. In a related project, there are also plans to construct the longest bike track in the UAE that will feature service facilities and rest stops and host international events and competitions.
Furthermore, there are plans to build multiple holiday homes and create ride-sharing services along with offering dedicated tourist coaches. All these will help boost tourism in the area.
Statutory Planning System
The statutory planning system updates not only the urban planning but also the plan hierarchies to maintain agility and consistency. The framework manuals and plans spell out the process of implementing the structural plans. The information details the spatial compliance to adhere to while the spatial map helps identify the location that developers need to address.
The structural framework is supported by zoning overlays that provide context to the investigations and policies under the structural plan. The zone plans help organize and outline the present and future locations where development activity is permitted. The plan maps the zones across Dubai and defines the kind of permitted use for each classification such as national housing, waterfronts, affordable housing, and transit-oriented development, among others.
Moreover, there are also planning overlays in place that provide additional data on how a particular area or site should be developed. These overlays are usually the outcomes of local area framework studies. They cover a bunch of topics ranging from economic development to strategic infrastructure, housing to land use, transportation planning to heritage conservation, and everything in between.
Encouraging Sustainable Living
Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan champions the cause of sustainable living. It focuses on creating integrated communities, sustainable housing, and sustainable mobility to reduce the carbon footprint and offer an eco-friendly lifestyle.
Lifestyle
The plan calls for the establishment of sustainable housing complexes that will be environmentally friendly. These houses will utilize renewable sources of energy, feature energy-efficient designs, and incorporate smart technologies.
To ensure residents have easy access to commercial centres, recreational facilities, and green spaces, these housing complexes will be part of larger integrated communities. Additionally, there are also plans to provide housing solutions that meet the diverse needs of citizens of varied backgrounds to help promote sustainable living standards in environmentally conscious neighbourhoods.
Transportation
The plan aims to promote eco-friendly transportation methods and prioritise public transportation as the primary mode of commuting throughout the emirate. As the plan intends to expand the reach of the public transportation network, including metros, buses, and trams, there will be less reliance on private cars, leading to less carbon emissions.
It also encourages sustainable mobility by making cycling lanes and walkways more accessible and safer for residents. Not only will it lead to less traffic, but it will also contribute to positive public health and foster a culture of sustainability.
Data-Driven Decision-Making and Transparency
One of the strengths of the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan is how strongly it is backed by scientific elements. As it incorporates an advanced data-driven system, it increases the odds of perfectly executing efficient urban planning. Additionally, it also helps in enhancing transparency in decision-making.
The plan calls for the creation of an all-inclusive planning database that utilizes data analytics to reinforce urban development. It relies on real-time data to track the needs of the emirate’s infrastructure, plan future projects meticulously, and forecast urban growth patterns effectively.
Not to forget, it also promotes transparency by providing the public access to urban planning decisions. This helps both the public and the stakeholders to get a detailed understanding of the decision-making procedure, and, in the process, fosters trust in the planning process.
Due to this innovative approach, the plan not only makes sure that the future development of the city is well-planned but is also adaptable to the needs of the ever-evolving population.
Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan vs. Other City Plans
What makes the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan stand out from the rest of typical city plans is that the former heavily emphasizes on creating a community-centric development through sustainable actions. Its vision to build a healthy and vibrant yet economically viable city distinguishes it from its peers.
In stark contrast to most other city plans, the Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan does not only strive for development for the sake of it. It wants to make conscious decisions by keeping in mind the impact on the environment. Hence, major focus is given to expanding green spaces and reducing the reliance on private vehicles by expanding public transportation.
To Conclude
The Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan is the ultimate blueprint for the emirate to prepare itself for the challenges of the next two decades. It forges the metropolitan areas and Hatta into a path of sustainable development. It prioritizes the prosperity, well-being, and happiness of the citizens through its people-centric approach. By working towards a sustainable future, it aims to create an environment where citizens, residents, and tourists can thrive.
This plan serves as a comprehensive future map for eco-friendly urban development. From providing affordable housing options, enhancing public transportation, conserving heritage sites, and boosting tourism, among others, this plan is paramount for Dubai to continue its global dominance as the ultimate career, shopping, travel, and residential destination in the world.
FAQs
More about Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan
What is the UAE Vision 2040?
The UAE Vision 2040 refers to a comprehensive guide for paving the way for sustainable urban development in the UAE. Through its Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan, it intends to make Dubai the best city to live in in the next two decades in terms of quality of life, economic growth, and sustainability.
How will Dubai look in 2040?
By 2040, Dubai aims to look like the ultimate eco-friendly urban city. With increased green spaces, sustainable housing options, enhanced public transportation, more job opportunities, and improved hospitality and retail sectors, the city will dramatically change from what it is today.
What is the Dubai Urban Master Plan?
Dubai Urban Master Plans are the framework guidelines that help the emirate forge a path of development. These plans have been in action since the 1960s and have over the past decades helped in coordinating and managing a structural plan approach through varied initiatives, strategies, principles, and policy directions.
What is the Dubai plan for 2050?
Dubai’s plan for 2050 primarily settles on achieving 75% of its energy requirements from clean sources. It wants to become a global hub for green economic practices. It wants to create a conducive environment for economic growth while also balancing the demand and supply with environmental obligations.
What is the main purpose of a master plan?
The main purpose of a master plan is to offer a comprehensive and long-term vision for the future development of a city or community. It helps to ensure the decision-making process is cognizant of providing a sustainable and cohesive outcome.
What is the difference between master planning and urban planning?
Master planning aims to offer a comprehensive and long-term vision for the future development of a city or community while urban planning encapsulates the wider development and management of urban areas, including community services, housing, land use, and transportation, among others.




